10 Revolutionary Medical Advances of the 21st Century Changing Lives Forever
The 21st century has been marked by remarkable advancements in medical science and technology, transforming the landscape of healthcare and offering new hope for treating diseases that were once considered incurable. From the revolutionary CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing technology to the rapid development of mRNA vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic, these innovations are not only extending lives but also enhancing the quality of life for millions of people worldwide.
As we explore this century’s major medical breakthroughs, a new era in medicine emerges. Personalized treatments, regenerative therapies, and AI are redefining healthcare and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
1. CRISPR-Cas9: Revolutionizing Gene Editing (2012-Present)

CRISPR-Cas9 technology has dramatically altered the landscape of genetic research since its introduction in 2012. This gene-editing tool, developed by Jennifer Doudna and Emmanuelle Charpentier, allows scientists to cut DNA at precise locations, enabling them to remove, add, or alter sections of the DNA sequence. CRISPR’s potential applications are vast, ranging from curing genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis and Huntington’s disease to combating viral infections such as HIV. In 2020, Doudna and Charpentier were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their groundbreaking work, solidifying CRISPR as one of the most significant medical advances of our time.
2. mRNA Vaccines: A New Era in Immunization (2020)
The COVID-19 pandemic brought mRNA vaccine technology to the forefront of global health. While research into mRNA vaccines had been ongoing for several years, it wasn’t until 2020 that the first mRNA vaccines were authorized for emergency use. Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna developed these vaccines using synthetic mRNA to instruct cells to produce a protein that triggers an immune response. This rapid development and deployment marked a turning point in vaccine technology, offering a new method that could be adapted quickly for various diseases. The success of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 has sparked research into their potential use for other viruses, cancers, and even autoimmune diseases.
3. Telemedicine: Expanding Access to Care (2020-Present)

The adoption of telemedicine surged during the COVID-19 pandemic as healthcare providers sought ways to safely continue patient care. Though telemedicine existed before 2020, the pandemic accelerated its integration into mainstream healthcare. Patients can now consult with doctors remotely, reducing the need for in-person visits, which is particularly beneficial for those with chronic conditions or limited mobility. Telemedicine has also made healthcare more accessible in rural and underserved areas, where medical facilities may be scarce. This shift has led to innovations in remote monitoring, digital diagnostics, and virtual care platforms, fundamentally changing how healthcare is delivered.
4. AI in Diagnostics and Drug Discovery (2010s-Present)

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly becoming a cornerstone of modern medicine. In the 2010s, AI began to make significant strides in diagnostics and drug discovery. For example, Google’s DeepMind developed an AI called AlphaFold, which in 2020 solved the decades-old problem of protein folding, a crucial step in understanding diseases and developing new drugs. AI-powered tools are also enhancing diagnostic accuracy in medical imaging, where algorithms can detect conditions like cancer, heart disease, and retinal disorders with remarkable precision. AI’s ability to analyze vast datasets quickly and accurately is helping to personalize treatment plans and expedite drug discovery processes, making it a vital tool in modern medicine.
5. Regenerative Medicine: Stem Cells and Beyond (2000s-Present)
Regenerative medicine has made significant advances since the early 2000s, with stem cell therapy leading the charge. Stem cells have the unique ability to develop into different types of cells, offering potential treatments for a wide range of conditions, from spinal cord injuries to heart disease. In 2013, scientists successfully grew a human liver from stem cells, marking a major milestone in organ regeneration. Research is also advancing in the field of tissue engineering, where scientists are developing lab-grown tissues and organs that could one day replace damaged or diseased ones, potentially eliminating the need for organ transplants.
6. Immunotherapy: A New Front in Cancer Treatment (2010s-Present)
Immunotherapy has emerged as one of the most promising new approaches to cancer treatment. Unlike traditional treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation, which attack cancer cells directly, immunotherapy works by empowering the body’s immune system to fight cancer. The 2010s saw significant breakthroughs in this field, with the approval of checkpoint inhibitors like pembrolizumab (Keytruda) in 2014, which have shown remarkable effectiveness in treating certain types of cancers. CAR-T cell therapy, another form of immunotherapy approved by the FDA in 2017, involves modifying a patient’s T cells to target and destroy cancer cells. These advances are not only prolonging lives but are also offering hope for long-term remission in some patients.
7. 3D Printing in Medicine: From Prosthetics to Organs (2010s-Present)

3D printing technology has revolutionized the medical field, offering unprecedented opportunities for creating custom prosthetics, implants, and even human tissues. In 2013, the first 3D-printed tracheal splint was used to save the life of a baby with a rare condition that caused his airways to collapse. Since then, 3D printing has been used to create customized prosthetics, dental implants, and surgical models, improving patient outcomes and reducing costs. Researchers are also working on bioprinting, where living cells are printed layer by layer to create tissues and organs, which could one day address the shortage of donor organs.
8. Microbiome Research: Understanding the Gut-Health Connection (2010s-Present)

The human microbiome, the collection of trillions of bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms living in and on our bodies, has become a focal point of medical research in recent years. Studies throughout the 2010s have revealed the microbiome’s crucial role in various aspects of health, including digestion, immunity, and even mental health. This research has led to the development of microbiome-based therapies, such as fecal microbiota transplants (FMT) for treating recurrent Clostridioides difficile infections. The ongoing exploration of the microbiome holds promise for new treatments for conditions ranging from obesity and diabetes to anxiety and depression.
9. Wearable Technology: Continuous Health Monitoring (2010s-Present)

Wearable health devices have evolved rapidly since the early 2010s, transitioning from simple fitness trackers to sophisticated health monitors. Modern wearables, such as smartwatches, can track heart rate, monitor sleep patterns, detect atrial fibrillation, and even measure blood oxygen levels. These devices are empowering individuals to take a more active role in managing their health and are also providing healthcare providers with continuous data that can improve patient care. The integration of wearable technology into healthcare represents a significant step toward personalized medicine and proactive health management.
10. Gene Therapy: Treating Genetic Disorders (2010s-Present)
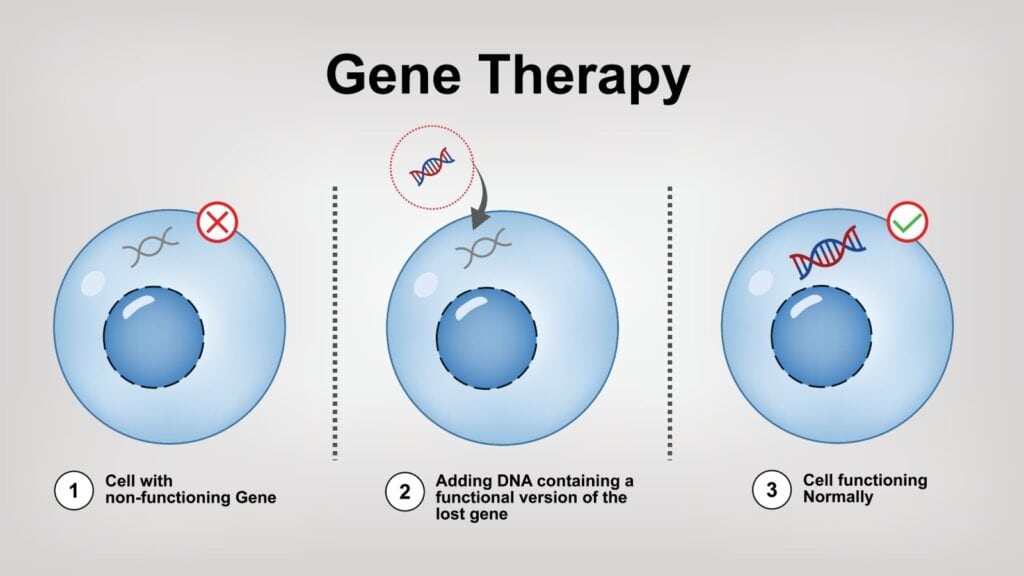
Gene therapy, which involves modifying or replacing faulty genes to treat or prevent diseases, has made significant strides in the past decade. In 2017, the FDA approved the first gene therapy for an inherited disease, Luxturna, which treats a rare form of blindness. Since then, several other gene therapies have been approved, targeting conditions like spinal muscular atrophy and certain types of leukemia. The ability to directly address the genetic root of diseases offers the potential for curative treatments, representing a major breakthrough in the fight against genetic disorders.
Conclusion

These advances are just a few examples of the remarkable progress being made in the medical field. As technology continues to evolve, the future holds even more promise for groundbreaking treatments and cures that could transform healthcare as we know it. The innovations of today are laying the foundation for a healthier, more personalized future in medicine.
Science Tells Us What To Expect As We Age: Strategies For Thriving In Later Life

How does aging affect our bodies and minds, and how can we adapt to those differences? These are questions that pertain to us all. Aging gradually alters people over decades, a long period shaped by individuals’ economic and social circumstances, their behaviors, their neighborhoods, and other factors. Also, while people experience common physiological issues in later life, they don’t follow a well-charted, developmentally predetermined path. Let’s take a look at what science has told us to expect. Read: Science Tells Us What To Expect As We Age: Strategies For Thriving In Later Life
3 Simple Somatic Movements You Can Do To Calm Your Nervous System

Daily life can be unnerving. And it’s easy to go from calm to anxious or nervous in a flash. What’s harder is to go from anxious or nervous to calm.These simple movements that I am going to share here have been found to successfully move an individual from a state of anxious nervousness to a state of calm. Read: 3 Simple Somatic Movements You Can Do To Calm Your Nervous System
Join Us

Join us on this empowering journey as we explore, celebrate, and elevate “her story.” The Queen Zone is not just a platform; it’s a community where women from all walks of life can come together, share their experiences, and inspire one another. Welcome to a space where the female experience takes center stage. Sign up for our newsletter so you don’t miss a thing, Queen!







