Science Tells Us What To Expect As We Age: Strategies for Thriving in Later Life
How does aging affect our bodies and minds, and how can we adapt to those differences? These are questions that pertain to us all. Aging gradually alters people over decades, a long period shaped by individuals’ economic and social circumstances, their behaviors, their neighborhoods, and other factors. Also, while people experience common physiological issues in later life, they don’t follow a well-charted, developmentally predetermined path. Let’s take a look at what science has told us to expect.
What Is Predictable?

“Predictable changes occur, but not necessarily at the same time or in the same sequence,” said Rosanne Leipzig, vice chair for education at the Brookdale Department of Geriatrics and Palliative Medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York. “There’s no more heterogeneous a group than older people.”
Leipzig, 72, works full time teaching medical residents and fellows and seeing patients. She has written a hefty 400-plus-page, information-packed book, “Honest Aging: An Insider’s Guide to the Second Half of Life.” It’s a comprehensive examination of what to expect in later life.
Getting Older Is Not a negative

Leipzig had two goals in writing this guide: “to overcome all the negatives that are out there about growing older” and “to help people understand that there are lots of things that you can do to adapt to your new normal as you age and have an enjoyable, engaged, meaningful life.”
Why call it “Honest Aging”? “Because so much of what’s out there is dishonest, claiming to teach people how to age backwards,” Leipzig said. “I think it’s time we say, ‘This is it; this is who we are,’ and admit how lucky we are to have all these years of extra time.”
Age 60 is not what it used to be

The doctor was referring to extraordinary gains in life expectancy achieved in the modern era. Because of medical advances, people over age 60 live far longer than people at the dawn of the 20th century. Still, most of us lack a good understanding of what happens to our bodies during this extended period after middle age.
Embrace the age your are

Several months ago, a medical student asked Leipzig whether references to age should be left out of a patient’s written medical history, as references to race have been eliminated. “I told her no; with medicine, age is always relevant,” Leipzig said. “It gives you a sense of where people are in their life, what they’ve lived through, and the disorders they might have, which are different than those in younger people.”
The Most Common Aging questions are…

What questions do older adults tend to ask most often? Leipzig rattled off a list: What can I do about this potbelly? How can I improve my sleep? I’m having trouble remembering names; is this dementia? Do I really need that colonoscopy or mammogram? What should I do to get back into shape? Do I really need to stop driving?
Underlying these is a poor understanding of what’s normal in later life and the physical and mental alterations aging brings.
Not everyone ages the same

Can the stages of aging be broken down, roughly, by decade? No, said Leipzig, noting that people in their 60s and 70s vary significantly in health and functioning. Typically, predictable changes associated with aging “start to happen much more between the ages of 75 and 85,” she told me. Here are a few of the age-related issues she highlights in her book:
Older Adults: Illness Presents Differently
Older adults often present with different symptoms when they become ill. For instance, a senior having a heart attack may be short of breath or confused, rather than report chest pain. Similarly, an older person with pneumonia may fall or have little appetite instead of having a fever and cough.
Medication Reactions Can Differ
Older adults react differently to medications. Because of changes in body composition and liver, kidney, and gut function, older adults are more sensitive to medications than younger people and often need lower doses. This includes medications that someone may have taken for years. It also applies to alcohol.
Your Energy Isn’t what it used to be

Older adults have reduced energy reserves. With advancing age, hearts become less efficient, lungs transfer less oxygen to the blood, more protein is needed for muscle synthesis, and muscle mass and strength decrease. The result: Older people generate less energy even as they need more energy to perform everyday tasks.
Hunger & Thirst Change

Hunger and thirst decline. People’s senses of taste and smell diminish, lessening food’s appeal. Loss of appetite becomes more common, and seniors tend to feel full after eating less food. The risk of dehydration increases.
Check your cognition

Cognition slows. Older adults process information more slowly and work harder to learn new information. Multitasking becomes more difficult, and reaction times grow slower. Problems finding words, especially nouns, are typical. Cognitive changes related to medications and illness are more frequent.
Flexibility Lessens

The musculoskeletal system is less flexible. Spines shorten as the discs that separate the vertebrae become harder and more compressed; older adults typically lose 1 to 3 inches in height as this happens. Balance is compromised because of changes in the inner ear, the brain, and the vestibular system (a complex system that regulates balance and a person’s sense of orientation in space). Muscles weaken in the legs, hips, and buttocks, and range of motion in joints contracts. Tendons and ligaments aren’t as strong, and falls and fractures are more frequent as bones become more brittle.
Eyes & Ears: get Them Checked
Eyesight and hearing change. Older adults need much more light to read than younger people. It’s harder for them to see the outlines of objects or distinguish between similar colors as color and contrast perception diminishes. With changes to the cornea, lens, and fluid within the eye, it takes longer to adjust to sunlight as well as darkness.
Hearing Is important
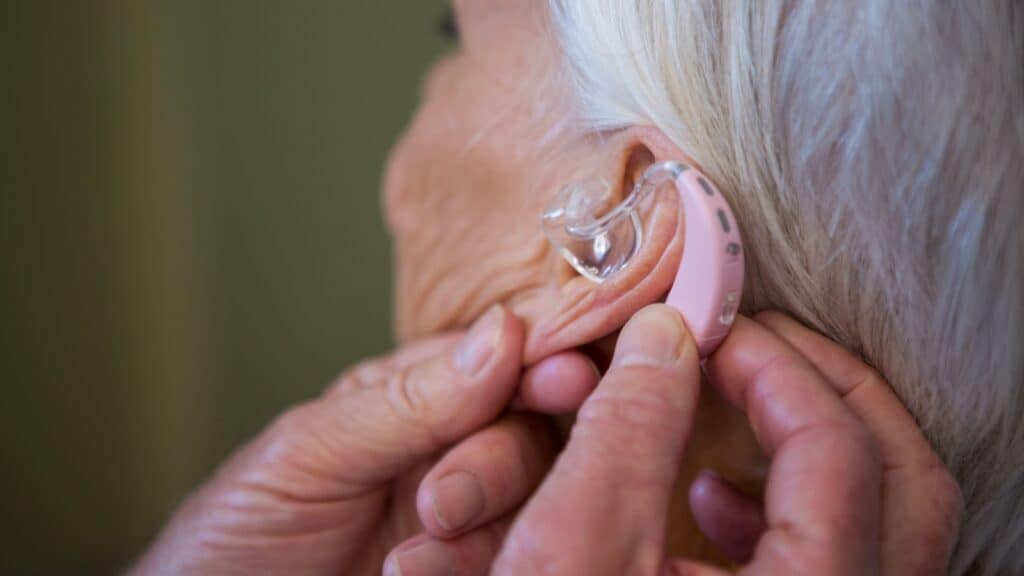
Because of accumulated damage to hair cells in the inner ear, it’s harder to hear, especially at high frequencies. It’s also harder to understand speech that’s rapid and loaded with information or that occurs in noisy environments.
Sleep Patterns Change

Sleep becomes fragmented. It takes longer for older adults to fall asleep, and they sleep more lightly, awakening more in the night.
Our Age Does Not have to define us

This is by no means a complete list of physiological changes that occur as we grow older. And it leaves out the many ways people can adapt to their new normal, something Leipzig spends a great deal of time discussing.
Take responsibility for health: be mindful of changes

A partial list of what she suggests, organized roughly by the topics above: Don’t ignore sudden changes in functioning; seek medical attention. At every doctor’s visit, ask why you’re taking medications, whether doses are appropriate, and whether medications can be stopped. Be physically active. Make sure you eat enough protein. Drink liquids even when you aren’t thirsty. Cut down on multitasking and work at your own pace. Do balance and resistance exercises. Have your eyes checked every year. Get hearing aids. Don’t exercise, drink alcohol, or eat a heavy meal within two to three hours of bedtime.
“Never say never,” Leipzig said. “There is almost always something that can be done to improve your situation as you grow older, if you’re willing to do it.”
This article was adapted by an article written by KFF Health News. KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
As You Age Your Self-Esteem Should Rise: Are You On Track?

In a society often fixated on youthfulness, aging is sometimes seen as a process to be dreaded. However, a recent study brings a refreshing perspective by highlighting that self-esteem tends to reach its zenith with age. According to a study published in the journal of the American Psychological Association, the age of 60 appears to be the prime time for self-esteem, and this positive trend can persist for a remarkable decade. Read: As You Age Your Self-Esteem Should Rise: Are You On Track?
Join Us

Join us on this empowering journey as we explore, celebrate, and elevate “her story.” The Queen Zone is not just a platform; it’s a community where women from all walks of life can come together, share their experiences, and inspire one another. Welcome to a space where the female experience takes center stage. Sign up for our newsletter so you don’t miss a thing, Queen!







