The U.S. Military’s Oath to the Constitution: What Happens If a President Acts Unconstitutionally?
The Trump administration has repeatedly undermined, dismantled, or threatened key democratic institutions that have upheld the U.S. government for nearly 250 years. From attacks on the judiciary, Congress, and the free press to challenges against election integrity, the Justice Department, and the rule of law itself, these actions have raised urgent concerns about the stability of American democracy.
When these institutional safeguards weaken or collapse, and a government openly defies the Constitution, the question arises: What is the military’s role in defending the nation from a rogue administration? Bound by an oath to protect the Constitution—not any individual leader—the military exists to serve the country, not enforce the will of a president. But with legal and structural limitations preventing military intervention in civilian governance, how far can—or should—the military go in resisting unlawful orders, upholding democracy, and protecting citizens from government overreach?
President’s Role in Military Command

As Commander-in-Chief, the President holds the highest position in the military chain of command, as established by Article II of the U.S. Constitution1. This authority allows the President to direct military operations and issue orders to the armed forces. However, this power is not absolute and is subject to important limitations:
- The President must issue only lawful orders that align with the Constitution and established laws.
- Military personnel are bound by their oath to disobey unlawful or unconstitutional orders.
- The Secretary of Defense, a civilian official, serves as a key intermediary between the President and military leadership.
- The Joint Chiefs of Staff advise the President on military matters but do not have direct command authority over troops.
These checks help ensure that presidential authority over the military remains within constitutional bounds and preserves the principle of civilian control over the armed forces.
Congress’ Oversight of Military Actions

Congress plays a crucial role in overseeing and regulating military actions, serving as a vital check on executive power. The Constitution grants Congress several key authorities:
- Declaring war and authorizing the use of military force
- Appropriating funds for military operations and personnel
- Establishing and maintaining the Uniform Code of Military Justice (UCMJ)
- Confirming high-ranking military officers and civilian leadership positions
- Conducting investigations and hearings on military matters
These powers allow Congress to shape military policy, influence strategic decisions, and hold the executive branch accountable for its actions in military affairs. For instance, Congress can limit or expand military operations through its control of funding and can investigate potential abuses or misconduct within the armed forces. This system of checks and balances helps ensure that military actions align with the nation’s interests and constitutional principles.
Military Oath to the Constitution

Military personnel swear an oath to “support and defend the Constitution of the United States against all enemies, foreign and domestic,” emphasizing their allegiance to the nation’s founding document rather than any individual leader or political party. This oath underscores the military’s commitment to upholding constitutional principles and the rule of law, even in potentially challenging situations. The significance of this oath is reinforced through education and training, particularly for young officers at institutions like West Point, where they learn about the importance of their constitutional allegiance and the ethical implications of their service.
Legal Limits on Military Intervention For Domestic Law Enforcement

The Posse Comitatus Act of 1878 significantly restricts the use of military forces for domestic law enforcement, requiring explicit Congressional authorization for such actions. This act, along with other legal frameworks, helps maintain the separation between military and civilian spheres. Exceptions exist for specific circumstances, such as responding to insurrections or enforcing federal law when authorized by the Constitution or Congress. The military’s domestic role is further regulated by various Department of Defense directives and instructions, which provide detailed guidance on permissible activities and proper procedures for domestic operations. These legal constraints ensure that military intervention in domestic affairs remains a last resort, subject to strict oversight and constitutional safeguards.
Military Limits on Acting Against A Sitting President

The U.S. military is legally constrained from acting against a sitting President, with strict limitations on its involvement in domestic affairs. The Posse Comitatus Act prohibits federal armed forces from executing civilian laws unless expressly authorized by the Constitution or Congress. This act effectively bars the military from engaging in law enforcement actions against U.S. citizens, including the President, without congressional approval.
In extreme circumstances, such as a national emergency or insurrection, the President may invoke the Insurrection Act to deploy troops domestically. However, this power is subject to judicial review and constitutional checks. The military’s primary recourse against potentially unlawful presidential orders is to refuse to carry them out, relying on their oath to the Constitution rather than to any individual. Any attempt by the military to remove a President or take control of the government without proper legal backing would itself be unconstitutional and illegal.
Challenging Presidential Orders

If a President issues an unconstitutional order, multiple safeguards exist to prevent its execution:
- Military leaders and personnel are bound by their oath to disobey unlawful orders, including those that violate the Constitution.
- The Secretary of Defense and Joint Chiefs of Staff can refuse to implement unconstitutional directives.
- Congress can pass legislation to overturn or defund executive actions.
- Federal courts, including the Supreme Court, can rule on the constitutionality of executive orders and issue injunctions to halt their implementation.
If institutional checks fail, state governments, public resistance, and civil disobedience may become the last line of defense against unconstitutional actions. However, determining an order’s constitutionality can be complex, often requiring judicial review to resolve disputes between branches of government.
Last Line of Defense

If all institutional checks fail to prevent unconstitutional actions by the government, the principle of constitutional resistance comes into play. This concept, rooted in the idea that the people have final authority over the Constitution’s meaning, allows for peaceable and provisional withholding of voluntary compliance with outrageous court decisions or government actions.
Constitutional resistance can take various forms:
- Civil disobedience: A public, non-violent, and conscientious breach of law aimed at bringing about change in laws or government policies.
- State-level resistance: Some states have implemented measures to resist federal overreach, such as the anti-commandeering doctrine, which allows states to refuse cooperation with federal officers.
- Nullification: A legal doctrine arguing that states have the ability to invalidate national actions they deem unconstitutional.
It’s important to note that these actions should be undertaken as a last resort and with careful consideration of potential consequences. The goal is to test the government’s actions in the wider political arena and ultimately restore adherence to constitutional principles. However, participants must be prepared to accept legal consequences as evidence of their fidelity to the rule of law.
Historical Examples of Military Defiance
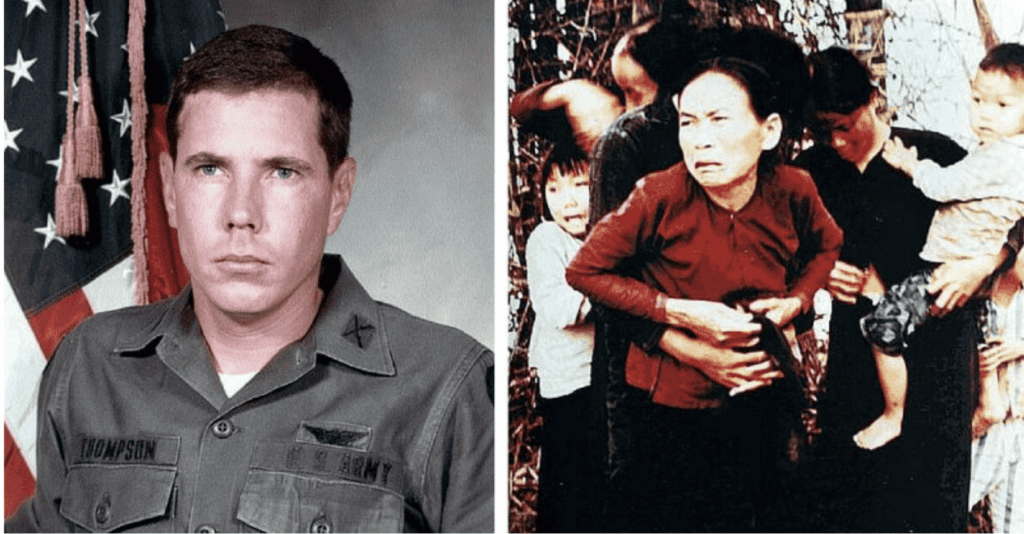

Throughout history, there have been notable instances of military personnel defying orders they deemed unlawful or unethical. These examples highlight the complex moral and legal landscape soldiers navigate when faced with potentially illegal commands:
- During the Vietnam War, U.S. Army Lt. William Calley ordered his men to massacre civilians in My Lai. Some soldiers refused to participate, with helicopter pilot Hugh Thompson Jr. even intervening to stop the killings. This incident led to significant changes in military ethics training.
- In 1968, Czech soldiers largely refused orders to suppress the Prague Spring, demonstrating that military loyalty to constitutional principles can supersede obedience to immediate superiors.
- More recently, U.S. Navy Secretary Richard Spencer resigned in 2019 after stating he could not “in good conscience obey an order” from President Trump regarding the case of Navy SEAL Eddie Gallagher. This illustrates how even high-ranking officials may feel compelled to disobey orders they believe violate their oath to the Constitution.
These cases underscore the importance of the military’s oath to the Constitution and the ethical obligation to disobey unlawful orders. However, determining the legality of an order can be complex, often requiring careful consideration of constitutional principles, military law, and international agreements.
Defending Constitutional Principles

The U.S. military’s commitment to defending the Constitution while maintaining civilian control is a delicate balance that forms the bedrock of American democracy.
This system relies on multiple layers of checks and balances, including:
- The oath of enlistment, which binds service members to support and defend the Constitution rather than any individual leader
- Civilian control shared across all three branches of government, ultimately expressed through the will of the American people in elections
- The principle that military officers must ensure any order they receive from the president is legal
- Congressional oversight through various mechanisms, including budget control and investigations
While the system is not perfect, it has largely succeeded in preventing military interference in civilian affairs throughout U.S. history. However, maintaining this balance requires ongoing vigilance, education, and commitment from both military and civilian leaders to uphold constitutional principles and the rule of law.
The Trump Administration’s Threat To Our Democracy Without Checks Or Balances

The recent actions of the Trump administration have raised significant concerns about the erosion of democratic institutions and the potential for constitutional crises. The administration’s moves to dismantle key government accountability mechanisms, such as firing inspectors general and pausing the enforcement of anti-corruption laws, signal a deliberate effort to remove constraints and oversight.
Additionally, the administration’s challenges to judicial authority and suggestions of bypassing established legal frameworks further threaten the balance of power that underpins American democracy. These developments underscore the importance of remaining vigilant in upholding the rule of law and the constitutional principles that have sustained the nation for nearly 250 years. The potential for significant constitutional turmoil looms if such actions continue unchecked.
What Trump’s Birthright Citizenship Plan Means for All Americans

This policy change would likely weaken the social fabric and sense of national unity, as it challenges the longstanding principle of inclusivity that has been a cornerstone of American society since the ratification of the 14th Amendment.
Based on reports from NBC News, President-elect Donald Trump has announced plans to end birthright citizenship and potentially deport American citizens born to undocumented immigrants, sparking debate over the constitutional and practical challenges of such a sweeping policy change.
READ: What Trump’s Birthright Citizenship Plan Means for All Americans
Join Us

Join us on this empowering journey as we explore, celebrate, and elevate “her story.” The Queen Zone is not just a platform; it’s a community where women from all walks of life can come together, share their experiences, and inspire one another. Welcome to a space where the female experience takes center stage. Sign up for our newsletter so you don’t miss a thing, Queen!